High-voltage cable ground monitoring system
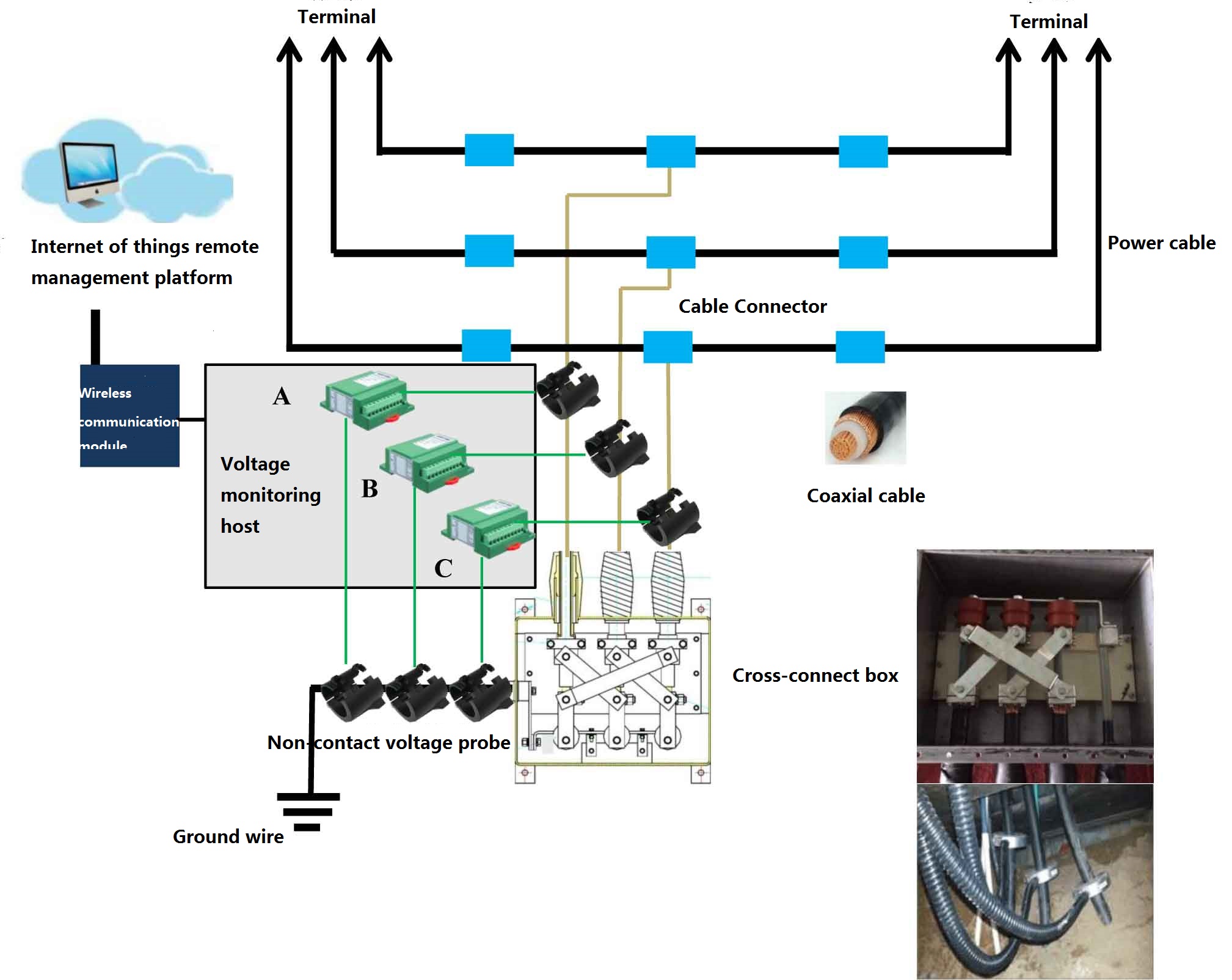
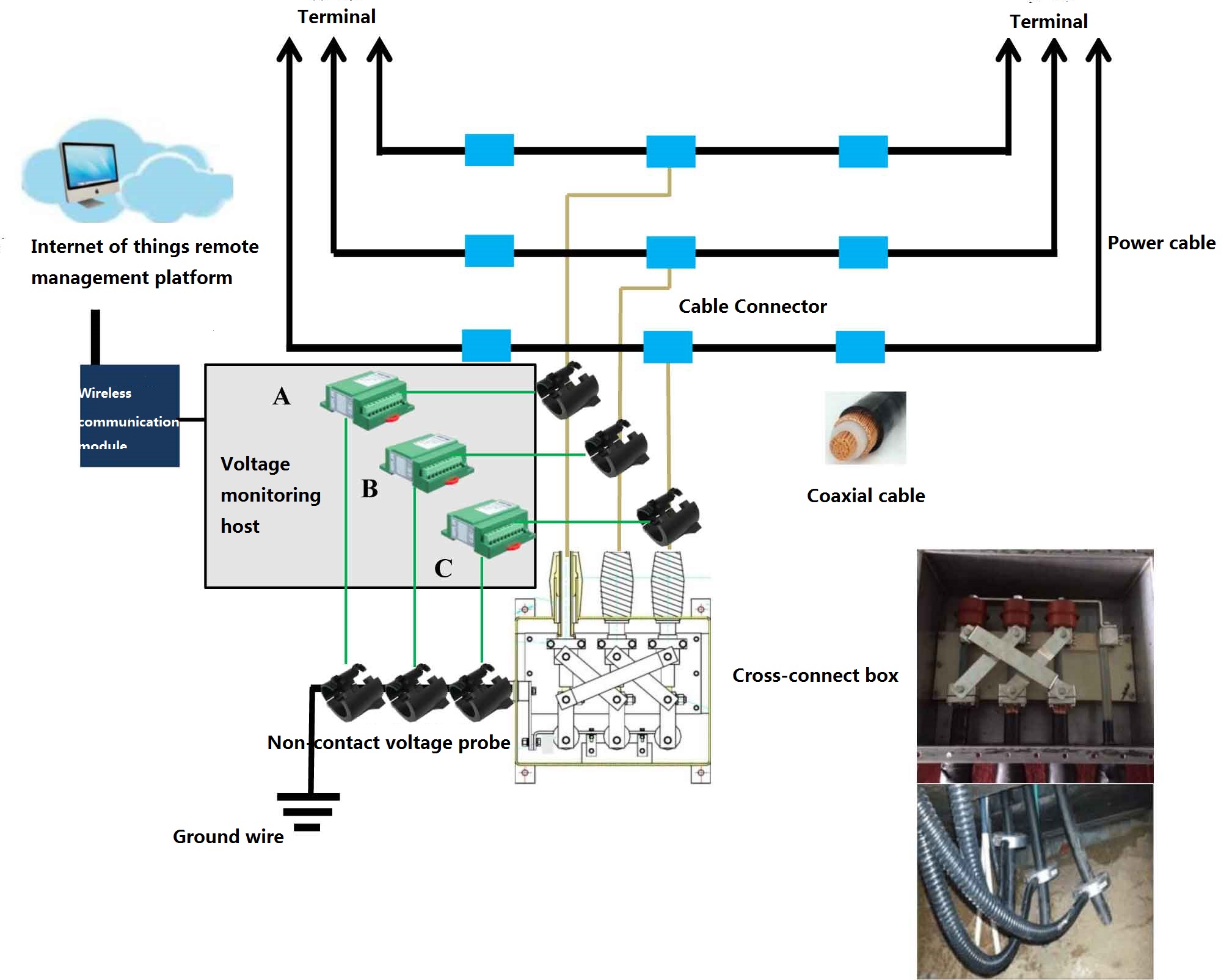
In the transmission of high voltage power cables, when the line is very long (more than 1000 meters), the sheath cross interconnection grounding method (ground cross interconnection box) is used. In this method, the cable line is divided into several large sections, and each large section is divided into three small sections of equal length in principle. Insulating joints are installed between the small sections. The three-phase jacket of the insulation joint is connected with the coaxial cable lead through the junction box. Normally, the operation status of the line is mainly based on regular inspection. Many insulation defects and potential faults cannot be found in time When the ground voltage exceeds the safe value, it will endanger the safety of patrolling personnel. Therefore, the use of accurate and fast fault finding technology to find the cable fault problem and eliminate the existing cable fault problem can play a positive role in the reliability and stability of power supply.
1. Non-contact voltage detection: it does not connect to the original line and does not affect the cable operation.
2. Real-time monitoring: real-time monitoring of the operating status of the cross-connect box to provide data basis for system failure judgment.
3. Operation and maintenance management of the power system: timely feedback on the type and location of the fault, and ensure the safety of maintenance personnel.
4. Maintenance management: abnormal alarm, fault type, intelligent scheduling.
5. The establishment of operation and maintenance mode: the effective and quantitative analysis of the big data of each monitoring is used to provide a reference for optimizing the operation line.
6. Efficient management: predict the potential failure risk according to big data, so that it can be replaced in time before the accident, quickly locate the fault location, and reduce the difficulty of maintenance.

1.1 Status:
1. Destruction by external force: After the high-voltage power cable is laid underground, it will be damaged by construction or other external forces, resulting in malfunction of the high-voltage line.
2. Quality problems: There are quality defects in the cable itself, resulting in malfunctions after being put into operation.
3. Construction process: The construction personnel did not strictly install the cable joints in accordance with the prescribed requirements, which brought potential safety hazards to the power transmission.
4. Grounding fault: The grounding box equipment is aging, which leads to grounding failure.
5. Manual inspection: According to the project requirements, the cycle plan inspection is inefficient.
6. National standard: 110KV route must be installed with grounding system monitoring.
1.2 Operational safety:
1. The ground fault causes the potential of the metal sheath of the cable to rise sharply to several thousand volts or even tens of thousands of volts, endangering the safety of maintenance personnel. When the outer sheath of the cable breaks down and continues to discharge at the breakdown point, the outer sheath of the cable is caused The temperature rises or even burns.
2. Quickly locate the fault point and replace manual inspection.
1.3 Necessity: Realize intelligent and visual monitoring and management of high-voltage cable comprehensive real-time monitoring:
1. Quantify, real-time, and judge the running status of the cable.
2. Fault location.
3. Ensure the safety of maintenance personnel.
4. Provide accurate information for maintenance and repair.
5. Establish operation model data and provide scientific management basis.
1.4 System functions
1. Comprehensive monitoring of high-voltage cables (partial discharge of cables, sheath current, ground voltage, cable temperature, anti-theft).
2. The voltage monitoring in the grounding box of the high-voltage cable sheath provides data basis for the system failure judgment.
3. Operation and maintenance management of the power system, timely feedback of the type and location of the fault, and guarantee the personal safety of maintenance personnel.

